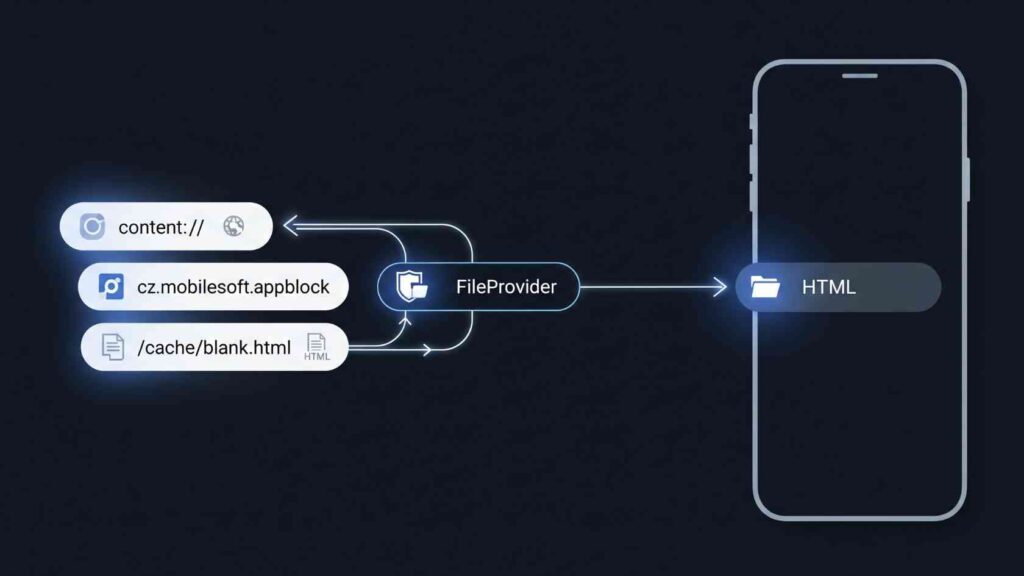
The URI content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html is a safe identifier. AppBlock, an Android app, uses it to handle temporary files that block distractions. AppBlock, made by the Czech firm MobileSoft, helps you work better by blocking specific apps and websites. This URI leads to a blank HTML placeholder in the app’s cache. Users often see it in logs or browser history. This can raise security queries. However, it is a regular part of Android’s file-sharing system.
What is AppBlock?
AppBlock is a working tool from MobileSoft s.r.o. that blocks distracting applications, websites, and notifications during focus sessions.
Key features are:
- Intelligent scheduling based on time or location.
- Usage analytics to track screen time.
- Specific modes that stop users from bypassing limitations.
The app uses Android’s Accessibility Services, VPN, and content restriction APIs to run efficiently in the background.
Breaking Down the URI Structure
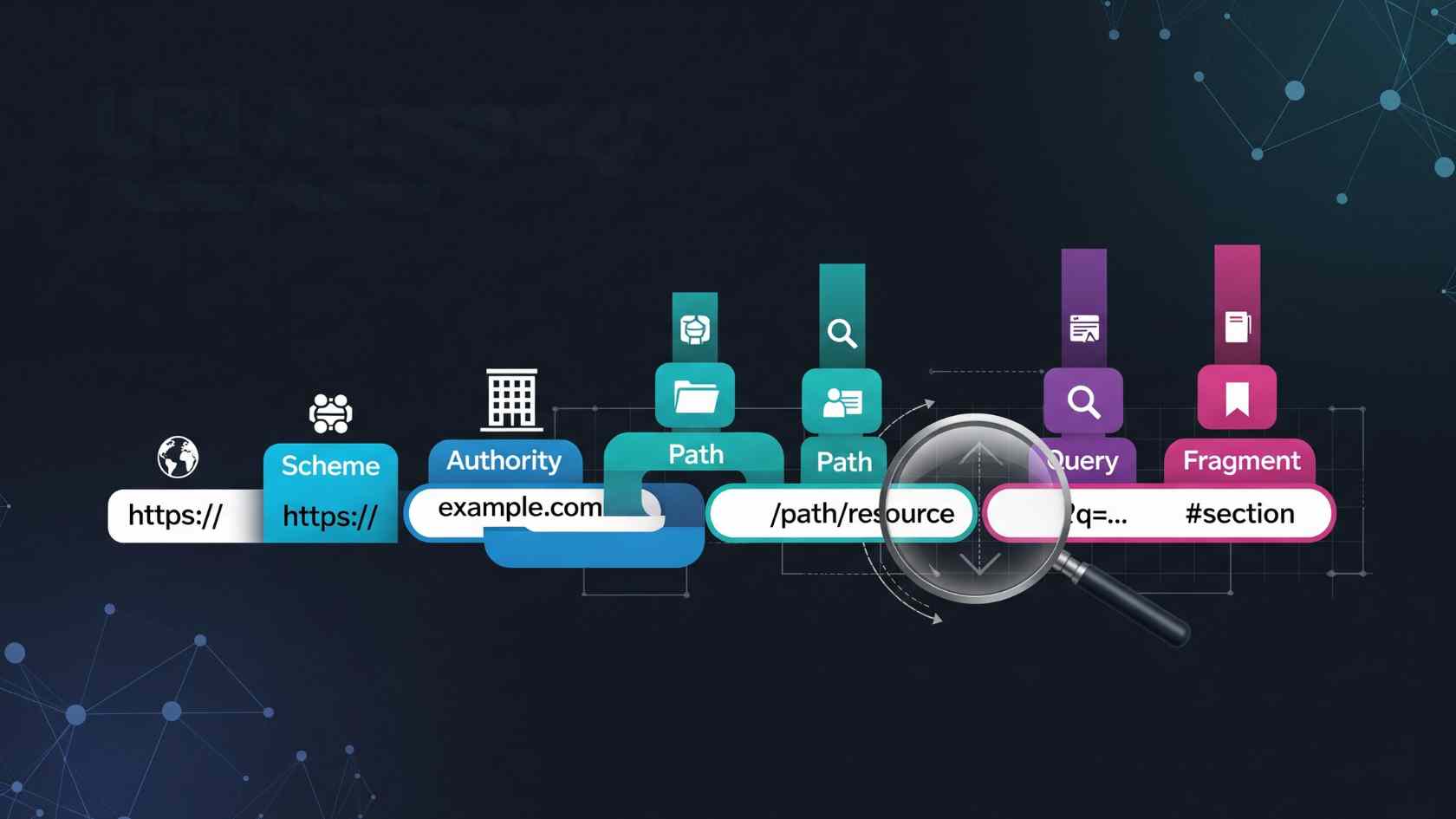
A content URI, like content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html, follows Android’s secure data access rules using ContentResolver. The “content://” prefix shows a managed resource. The “cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider” part identifies AppBlock’s FileProvider component. The path “/cache/blank.html” points to a temporary HTML file in the app’s cache. It’s made for quick, short-term storage.
This structure hides the file paths. This prevents direct access and keeps sensitive data safe. Android set stricter rules after version 7.0. It now requires content URIs instead of file:// paths. This change helps prevent FileUriExposedException errors. FileProvider acts as a gatekeeper, granting limited permissions only when needed.
Role of FileProvider in Android
FileProvider is a type of ContentProvider. It allows apps to share files securely without showing their internal storage paths. In AppBlock, the app adds the entry “cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider” to the AndroidManifest.xml. It sets exported=”false” to boost privacy. It creates content URIs for cache files. It works with scoped storage to meet modern Android security needs.
Developers configure it via XML paths like <cache-path name=”cache” path=”.” />, allowing controlled access to temporary directories. This setup fits AppBlock’s needs. It will enable temporary URI permissions with flags such as FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION. Overall, it maintains sandbox isolation while facilitating essential operations.
Purpose of a Blank HTML File
The blank.html file serves as a simple placeholder. When AppBlock blocks content, it shows an empty page. This helps avoid distractions. It loads instantly from cache, so there are no network calls. This boosts performance and stops scripts and ads from running. This design ensures WebView components remain stable, preventing crashes during redirects.
AppBlock recreates the file when needed. This follows Android’s cache rules, which precise temporary data when storage is low. It supports distraction blocking by neutralizing sites seamlessly, promoting focus without user frustration.
How AppBlock Uses This URI

When a user tries to visit a blocked site, AppBlock steps in using WebView. It shows content from content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html. This redirection keeps the interface tidy by hiding the block behind a proper HTML response. The URI shows up in logs when debugging, using the app, or running system scans. It stays internal unless someone shares it directly.
Developers should use ContentResolver. openInputStream(uri) instead of file paths. This helps prevent FileNotFoundException. AppBlock’s architecture uses background threads for these operations, keeping the UI responsive.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Users see blank screens when blank.html is missing. This can occur due to cache corruption, OS updates, or sudden shutdowns. A SecurityException may occur due to permission mismatches, which can be resolved by adding URI flags. FileNotFoundException in WebView stems from treating content URIs as files; enable setAllowContentAccess(true).
To fix this, clear AppBlock’s cache. Go to Settings > Apps > Storage, then tap Clear Cache. This will regenerate the files while keeping your settings. Reinstalling after a backup resolves persistent issues with high success rates. Verify storage permissions and restart for quick recovery.
Issue Symptoms Fix
- Missing blank.html , White/blank screen on blocks , Clear cache
- SecurityException Permission denial logs. Add FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION.
- FileNotFoundException Logs during WebView load Using ContentResolver
Security and Privacy Aspects
This URI poses no threat; it’s sandboxed and inaccessible to other apps without grants. FileProvider’s exported=”false” and path validation prevent traversal attacks. No personal data is exposed, as blank.html contains minimal content.
Android’s permission system ensures safety, with cache files auto-managed. Download AppBlock from official sources, such as the Google Play Store, to avoid risks. Developers should revoke permissions post-use and validate inputs.
Performance Optimizations and Best Practices for Developers
Using minimal HTML reduces load times and memory usage, making it ideal for mobile. Try-with-resources handles InputStreams to avoid losses. Background threads prevent ANR during access. AppBlock’s cache choice optimizes resources, as the system handles cleanup. This lightweight approach supports battery life and smooth blocking.
Declare unique authorities matching code, including grantUriPermissions=”true.” Define precise paths in res/xml/paths.xml. Test across Android versions for scoped storage compatibility. Avoid broad paths; use canonicalization against “../” sequences. Monitor logs for exceptions during integration.
Why It Appears in Logs or History
Scanners, cleaners, or debug tools detect content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html in WebView caches or reports. It logs during blocks or crashes if files are corrupt. No action needed; it’s benign system behavior.
Also Read: OCA0188 Error — What It Means and How to Fix It
Conclusion
The URI content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html points to a basic HTML file. This file is used by the AppBlock app to block websites. It is not a threat, not malware, and not an internet link. It exists solely to display a blank screen when AppBlock prevents access to a webpage.
Understanding Android’s content URIs, how AppBlock uses blank.html, and why this path shows in your device’s browser helps clear up any mess. This means that content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html is a standard and safe way for AppBlock to manage digital distractions.