Bandwidth sharing is an emerging form of passive income where individuals allow others to use their excess internet bandwidth in exchange for compensation. This method is gaining popularity in monetising and underutilising internet resources without requiring significant effort.
It functions because many internet users, particularly those with high-speed connections or unlimited data plans, do not consume all the bandwidth, as they are allocated by their internet service provider (ISP).
By sharing this unused bandwidth with external parties, they can generate a steady stream of income with minimal involvement.
How Bandwidth Sharing Works
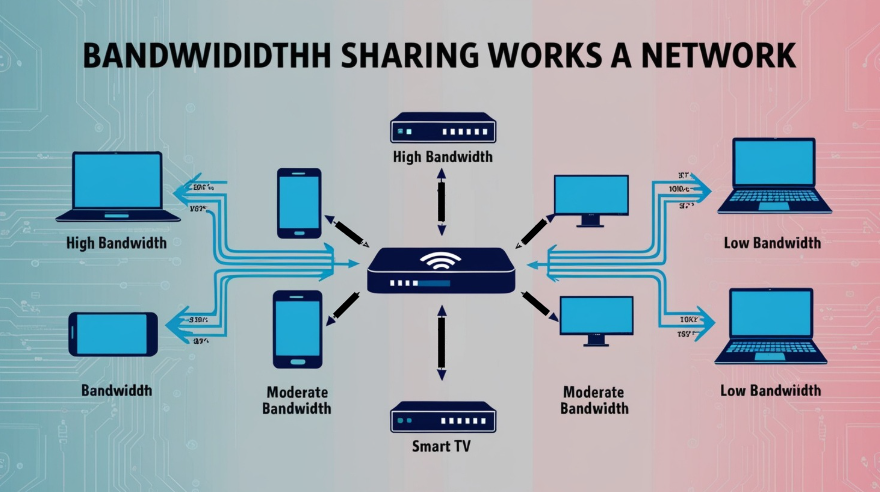
Bandwidth sharing is based on a network of users who contribute their internet connection to a certain platform or service. When anyone “shares” his bandwidth, he is allowing others to route data through his internet connection. In essence, this is internet sharing.
This is accomplished by making use of specialized applications or software provided by the bandwidth-sharing platforms themselves. Applications like this usually run in the background of a device. They route part of the incoming bandwidth for use by third-party clients. The system distributes data traffic across many network participants. This helps meet increased bandwidth demands for special purposes more effectively.
Participants are paid based on the amount of data shared, their availability, and the demand for bandwidth in their geographical location. The payoffs are often very minimal, and over time, they amass as the provider continues sharing his online resources.
Other clients who may need shared bandwidth include businesses and individuals seeking extra capacity. This can be for various reasons, such as bypassing regional content restrictions, testing websites or applications in different countries, or accessing distributed networks for data collection.
This approach benefits companies by decentralizing internet traffic routing. It is a more cost-effective and scalable solution than traditional methods, like purchasing additional bandwidth directly from ISPs.
Real-World Uses of Shared Bandwidth
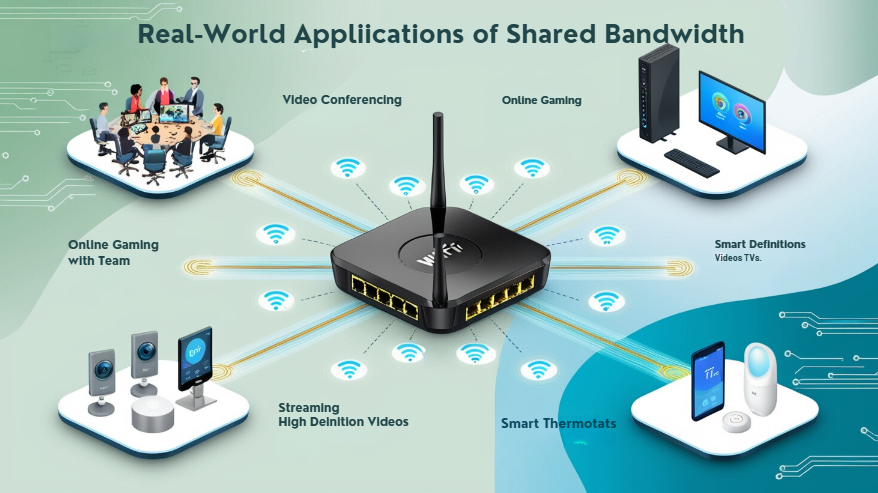
There are several use cases in which consumers make use of bandwidth-sharing services. Among the most common use cases is that of CDNs, or content operating companies that are geographically dispersed.
These companies can make use of bandwidth-sharing platforms to ensure their content is being delivered efficiently across users in different parts of the country, enabling performance optimisation and latency reduction.
Another good example is web scraping or data aggregation for businesses. With the use of such services, a business in need of information from several sites can route its requests through shared bandwidth nodes.
In this way, it would not be IP-blocked because too many requests would come from just one IP address. It routes traffic through a distributed network of individual bandwidth contributors so that businesses can scrape off data with no alarms or interruptions.
In other cases, bandwidth sharing is also applied for research purposes, to study internet performance in different regions. This might include researchers or companies testing network speeds, latency, or availability by tapping shared bandwidth from users worldwide.
This is much more representative of global internet infrastructure and performance metrics than could be reaped using data from one location or ISP.
Companies Offering Bandwidth Sharing Services

Several companies are into bandwidth-sharing services, creating avenues through which people can sell their excess bandwidth in exchange for money. Among the key vendors in this include:
1. Honeygain
This is a platform that enables users to share their internet through the execution of a small application on any of their devices. Honeygain forwards client requests, such as web scraping or market research jobs, through the user’s bandwidth. In return, the user receives a monetary return dependent on the level of traffic they can provide.
2. PacketStream
Just like Honeygain, PacketStream lets users sell unused bandwidth. It is utilized for web scraping and showing geo-restricted content. Users are paid for bandwidth contributed, and the dashboard shows the amount used and the earnings brought in.
3. Peer2Profit
Much like the others, this is another bandwidth-sharing service wherein the clients of said bandwidth are paying the users for usage.
The system functions much like any other described so far, offering its services to businesses that require additional bandwidth for activities such as data gathering or content delivery.
How to Share Bandwidth
Bandwidth sharing is pretty easy to do as most of the platforms try to make the setup as painless as possible. First of all, a person selects any reputable bandwidth-sharing services and then creates an account.
After the registration, the user has to download and install the platform’s proprietary software on his computer, phone, or other device connected to the internet.
The software bridges the two, enabling third-party clients to connect with the user’s bandwidth while security and privacy are preserved. Once installed, the application sits in the background, rerouting some of the user’s unused bandwidth to clients.
Most allow the user, within the application settings, to adjust exactly how much bandwidth is shared, letting them decide how much of their Internet connection they want to give out.
Usually, on all such platforms, a dashboard will be provided to the user, showing his bandwidth usage, earnings, and other important metrics. Notably, bandwidth sharing does not easily conflict with the personal use of the internet by a user. Most of these platforms are coded in a manner that they run when your bandwidth is not utilised or out of periods of activity.
Users with limited data plans or slow speeds should; however, exercise caution since bandwidth sharing results in data consumption and may attract overage fees from your ISP. Users must also be made aware of their respective legal or contractual limitations imposed by their ISP regarding bandwidth sharing.
Things to Consider for Bandwidth Sharing
That said, though it may seem like an effortless and passive way to earn an extra buck, bandwidth sharing does have some considerations.
The most important factor is that the money earned largely correlates to how much bandwidth one can give out. It also depends on the demand for this bandwidth in the area concerned.
Earnings will be limited. It’s not a way to generate substantial income on its own. Instead, it’s one of many supplemental income sources. Users can leverage their existing internet connection to earn small incremental payments over time.
Besides this, privacy and security are paramount. While the overwhelming majority of reputable platforms are adopting encryption and other security measures, participants need to feel comfortable knowing that a portion of their internet connection will be used by third-party sources.
This makes it crucial to cultivate trust. The platform must uphold highly valued privacy standards and maintain transparency about how the bandwidth will be used.
Also Read: Choosing a Web Hosting to Support Business Growth
Lastly,
Last but not least, the influence of bandwidth sharing should be considered in the whole usage experience.
Different platforms are designed to run smoothly with minimal disturbance. However, heavy bandwidth-sharing activities can slow down a user’s connection, especially if they have a lower-speed internet plan.
It’s important to track performance and adjust settings as needed. This helps maintain a balance between personal use and bandwidth sharing.